
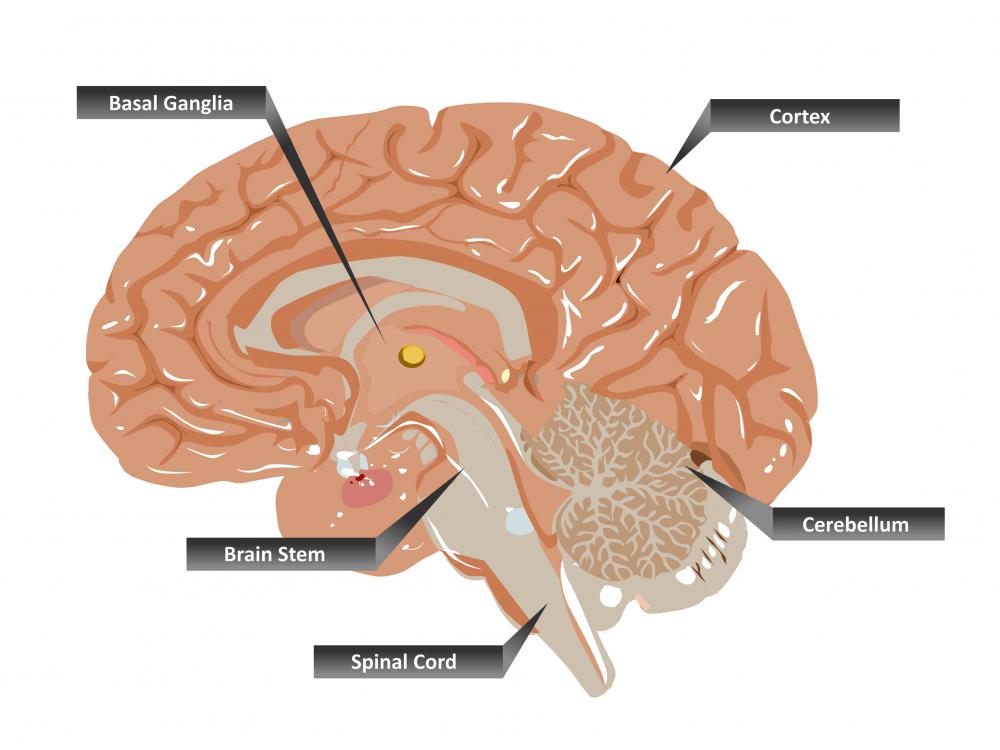
In addition, part of the nucleus accumbens core is centrally involved in the induction of slow-wave sleep. As a whole, the nucleus accumbens has a significant role in the cognitive processing of motivation, aversion, reward (i.e., incentive salience, pleasure, and positive reinforcement), and reinforcement learning (e.g., Pavlovian-instrumental transfer) hence, it has a significant role in addiction. These substructures have different morphology and functions.ĭifferent NAcc subregions (core vs shell) and neuron subpopulations within each region ( D1-type vs D2-type medium spiny neurons) are responsible for different cognitive functions. Each cerebral hemisphere has its own nucleus accumbens, which can be divided into two structures: the nucleus accumbens core and the nucleus accumbens shell. The dopaminergic neurons of the mesolimbic pathway project onto the GABAergic medium spiny neurons of the nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle. The ventral striatum and dorsal striatum collectively form the striatum, which is the main component of the basal ganglia. The nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle collectively form the ventral striatum. The nucleus accumbens ( NAc or NAcc also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the nucleus accumbens septi, Latin for " nucleus adjacent to the septum") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypothalamus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
